Your Best Blood Glucose Guide in 2023

Why is it so important to manage blood glucose levels (amount of sugar in your blood) and take regular blood glucose measurements for certain people?

For example, diabetics may need to monitor their levels using a blood glucose monitor or glucometer.
In this article, we discover more about this key sugar in our bodies and the consequences of failing to manage it!
What Is Blood Glucose?
Blood glucose (blood sugar) in your body is the main sugar that exists in your blood.
We get this sugar from what we eat and drink and it makes up our body’s leading energy source. Our blood carries glucose to all of our body cells to be used for energy.

For example, our brains use up half of the available sugar energy in our bodies because it is rich in nerve cells (neurons).
What Does Blood Glucose Tell You?
Your blood glucose levels tell you how much sugar you have in your blood.

It is important to ensure that you have the recommended amount of blood glucose without spiralling out of control or before it reaches unhealthy levels.
How Do You Measure Blood Glucose Levels?
You can use a blood glucose monitor or glucometer to measure your blood glucose levels. We advocate buying your own device to perform self-monitoring of your blood glucose levels.
Home glucometers usually display the results in either plasma or whole blood values. Understanding the type of value your glucometer provides can help you compare your home test results with those done by your preferred doctor.
When Is the Best Time to Check My Blood Sugar?
These are the best times of the day recommended to check your blood sugar:
- Before or 2 hours after your meals
- Before or after exercise
- When you are unwell
- When you feel hungry, giddy, confused, or sweaty
If you are unsure, you can always check with a medical professional.
How to Use a Blood Glucose Monitor? Basic Instructions
There are many brands of blood glucose monitors available in the market today.
Instructions for blood glucose monitor usage:-
- Before taking your blood glucose measurement, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. Pat dry
- Insert a test strip into the glucometer
- Squeeze your finger
- Use a lancet to prick the side of your finger
- Squeeze 1 drop of blood out
- Put the drop of blood onto the test strip and make sure that it is big enough
- Record the blood glucose reading that appears
- Discard used lancets properly in the rubbish bin
What Are the Best Blood Glucose Monitor and Glucometer Brands in Singapore?
Just starting out on self-monitoring of your blood glucose to keep your levels under control? Here are some of the easiest blood glucose monitors to use:
- CareSens
- Roche
- Lovia
- Accu-Chek (Aviva)
- OneTouch Verio
Where to a Buy Blood Glucose Monitor in Singapore
Where can you buy a blood glucose monitor or a glucometer in Singapore?
There are a few places that sell blood glucose monitoring devices, like:
- Polyclinics under the National Health Group (NHG)
- Guardian
- Watsons
- NTUC Fairprice (Giant and Cold Storage supermarkets do not sell the device)
You can also buy your CareSens glucometer and blood glucose monitoring accessories on SeniorCare, one of Singapore’s leading elderly-care e-stores! SeniorCare provides good rates, fast delivery and responsive services.
Blood Glucose Conversion Chart
Some regions in the world use mmol/L as a measurement unit for blood glucose, while others may use mg/dL instead. It can be confusing if you’re looking at 2 different charts with each unit.
The easiest way to convert mmol/L to mg/dL is to multiply the figure in mmol/L by 18.

What Are the Normal Blood Glucose Levels in Singapore for Adults?
Everyone’s blood glucose level differs slightly, but you can take this guide as a reference for a normal range:
- Before meals: 80 – 130 mg/dL
- 2 hours after meals: <180mg/dL
You should also take a look at your fasting blood glucose, which refers to your blood sugar measurement after an overnight fast where you don’t eat.
These are the normal fasting blood glucose levels:
- 99mg/dL or lower
What Are the Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating?
When you determine the normal range of blood glucose levels, you need to consider your readings before and after a meal.

As mentioned above, normal blood sugar levels after eating should be less than 180mg/dL.
What Level of Blood Glucose Is Dangerous?
Blood glucose levels of 300mg/dL are dangerous.
Take a look at this chart for a summary:
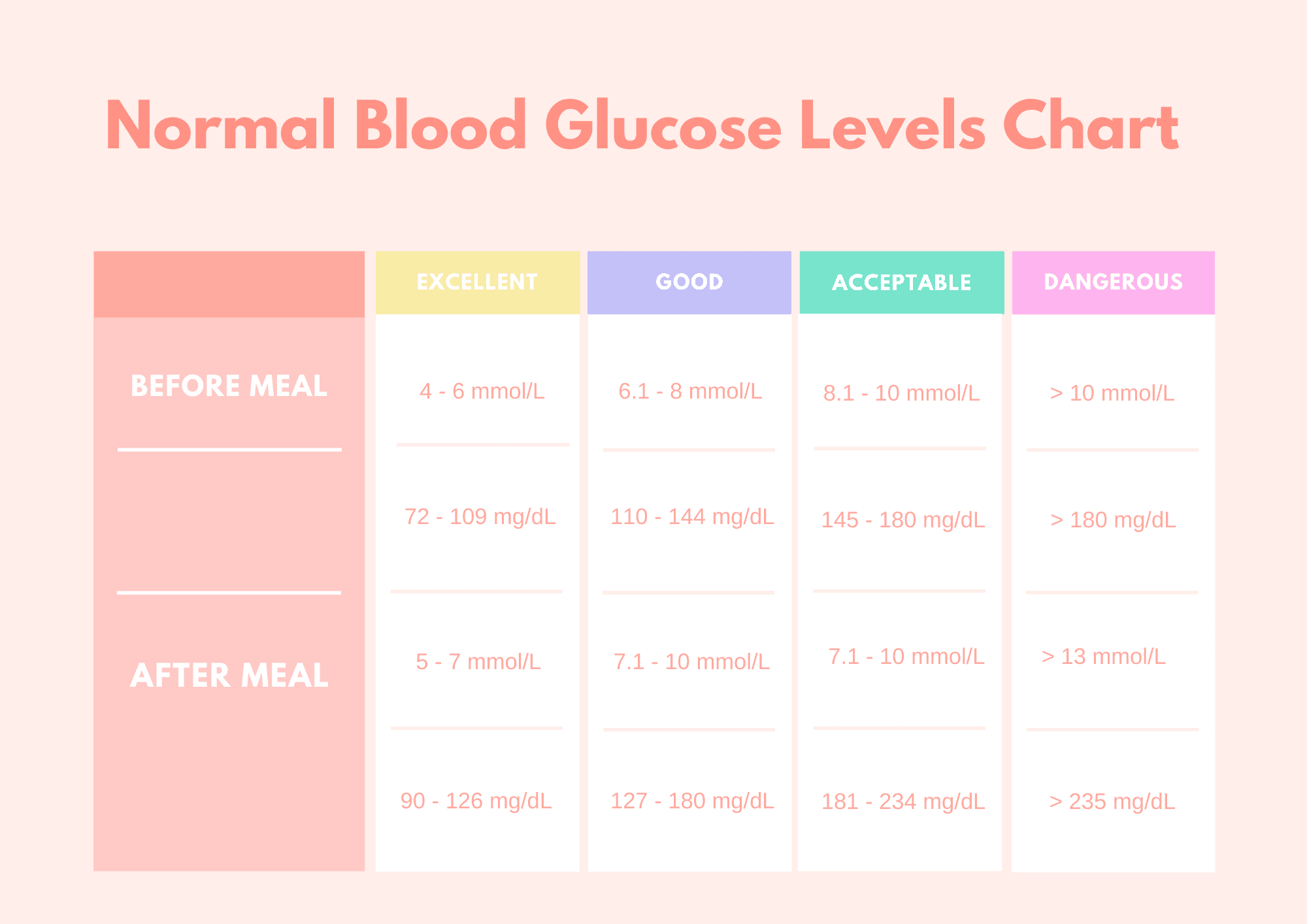
For fasting blood glucose, these are the unhealthy levels to look out for:
- 100 -125mg/dL means that you have prediabetes
- 126mg/dL or higher means that you have diabetes
What Do High Blood Glucose Levels (Hyperglycemia) Mean?
Having a high blood glucose level is a condition referred to as hyperglycemia.
This means that there is excessive sugar in your blood because of a lack of insulin, or when your body cannot use it properly. Insulin is the hormone responsible for transporting glucose in the blood.
What Are the Symptoms of Hyperglycemia?

Hyperglycemia is linked to diabetes and can lead to symptoms like:
- Vomiting
- Excessive thirst and hunger
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Skin infections
- Vision problems
- Rapid heartbeat
Untreated hyperglycemia can lead to these serious complications after long periods of time:
- Nerve damage (which can lead to kidney and eye damage, as well as wounds that don’t heal)
- Blood vessel and tissue damage (blood vessel damage can cause a higher risk of heart attack and stroke)
- Organ damage
What Are the Risk Factors of Hyperglycemia?
Some risk factors can increase your likelihood of developing hyperglycemia.

They include:
- A family history of Type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure or cholesterol (read how high blood pressure is linked to diabetes here)
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
- A history of gestational diabetes (diabetes developed during pregnancy)
- Obesity
- Asian American, Native American, and African American races
How to Lower High Glucose Levels
Before your high glucose levels progress to other severe health complications, it’s important to actively manage and control it.
There are some methods that you can use to reduce your sugar levels:
Eating Cinnamon Lowers Blood Sugar
Cinnamon is a common spice that has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).

Eating cinnamon can reduce fasting blood glucose levels and signal insulin release to bring down high sugar levels. This applies whether you are eating cinnamon sticks or extracts.
Control Your Carbohydrate Consumption
How much carbohydrates you eat has a strong impact on your blood glucose levels.
Therefore, it is advised to manage the amount of carbohydrates you eat by being aware of how much you need and by counting them.

This may help you plan your meals correctly and boost blood sugar management.
Drink Enough Water
Water is essential for life.

It aids in preventing dehydration and helps your kidneys flush out excess sugar via your urine. It may also rehydrate your blood, reduce blood sugar levels, and lower your risk of diabetes.
High Blood Glucose and Diabetes
People suffering from diabetes may also develop high blood glucose if the body creates too much insulin. Insulin is a type of hormone that functions to allow glucose to enter your cells to create energy.
Diabetes is a lifelong disease that has no cure. Instead, you need to manage it in these ways:
- Insulin injections
- Healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Oral medication
- Constant monitoring and control of blood sugar
How to Test for Diabetes in Singapore
There are a few ways to test whether you have diabetes in Singapore.

- Fasting glucose test
- Casual glucose test
- OGTT
- Glycated haemoglobin test (HbA1c)
You can also get tested for diabetes at most GP clinics.
What Is the Meaning of HbA1c?
In 2019, the Ministry of Health (MOH) approved the use of the HbA1c test as an alternative diabetes screening test.
If you’ve come across the term when assessing your blood glucose levels, it refers to your average blood glucose or sugar levels over the last 2 – 3 months.
During this test, a blood sample will be extracted from your arm.
What Is the Normal Range of HbA1c?
Those with diabetes should have an ideal HbA1c level of about 48mmol/mol or lower.
On the other hand, if you are at risk of developing Type 2 diabetes, you should be aiming for a range below 42mmol/mol.
How to Interpret the HbA1c Test
According to survey data by the MOH, here is how to interpret the readings:
- 6.0% and below: no diabetes
- 6.1% – 6.9%: body may not be able to regulate blood sugar properly; further testing required
- 7.0% and above: presence of diabetes
What Are the Common Types of Diabetes?
There are 2 common types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2.
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition where the pancreas cannot create enough insulin, or doesn’t produce any at all. There are a few factors that can contribute to Type 1 diabetes:
- Genetics
- Exposure to environmental factors and viruses
While the condition typically happens in children or teenagers, it can also develop in adults.
What Is Pre-diabetes?
Prediabetes is a health condition where you have blood glucose levels that are higher than the recommended normal range, but have not reached the point of Type 2 diabetes.
However, if you fail to make lifestyle changes, both children and adults are at high risk of getting Type 2 diabetes. Thankfully, you can still stop the progression by managing your condition.
Prediabetes usually doesn’t come with symptoms, but if your condition has worsened to Type 2 diabetes, you may experience the same signs.
What Is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is high blood glucose that happens during pregnancy. It usually goes away after birth, and can affect women who have never had diabetes before.
This condition can affect your baby’s health and increase your risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later on. It usually happens during the second-half of your pregnancy, and you will most likely only discover it after going for an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT).
This test involves drinking a bottle of glucose solution and taking 3 blood glucose measurements.
What Are the Diabetes Statistics in Singapore?
Diabetes isn’t just a risky health problem – it’s also expensive to manage.
In fact, it costs Singapore more than S$1 billion (US$735K) a year to manage it. Thanks to this, it has long declared war on diabetes.

Despite this, there was a minor increase in diabetes in Singapore from 2019 to 2020 (9.5%), as compared to 2017 (8.8%).
The number of diabetics above the age of 40 by 2030 is expected to hit 600,000 Singaporeans.
What Are the Health Dangers and Complications of Diabetes?
There are a few complications of diabetes:
- Blindness (diabetes damages the retinal blood vessels and raises the risk of other related conditions like glaucoma and cataracts)
- Vascular dementia (poor blood supply causes the death of brain cells and a loss of brain function)
- Arterial disease (diabetes obstructs the process of maintaining and protecting healthy blood vessels in the body, therefore leading to hardening and narrowing of blood vessels)
- Nerve damage (excess sugar harms the walls of capillaries, tiny blood vessels that enrich the nerves, and may lead to complications like damage to the gastrointestinal tract and even erectile dysfunction)
- Kidney disease (your kidneys have millions of tiny blood vessel clusters that sift out waste from your blood in a process that can be damaged by diabetes, leading to kidney failure)
- Pregnancy complications (high sugar levels can hurt both the mother and baby, and when uncontrolled, may increase the risks of miscarriage, birth defects, stillbirth, pre-eclampsia, diabetic eye problems and more)
If you suffer from diabetes, you are at a higher risk of lower limb amputation, which is a serious complication of the condition. This happens when wounds or ulcers fail to heal.

Failure to heal can lead to tissue damage or death, also known as gangrene. Existing infections may spread to your bones.
If the infection cannot be stopped or if the damage cannot be reversed, amputation may be required.
How Can People With Diabetes Control Their Condition?
Diabetes cannot be cured, and this applies to whether you have Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes. Therefore, it is important to keep your condition under control.
As mentioned above, here are some ways:
Healthy Diet Changes
What are the best foods for diabetics in Singapore, and how can you successfully control your blood sugar with your diet?

It’s important to watch what you eat. If you have diabetes, you might be wondering about eating certain foods, like soy milk and jackfruit, which are rumoured to be good for diabetes.
Here are some types of food that are good for people with Type 2 diabetes:
- Vegetables (green peas, kale, onion, lettuce, celery, cauliflower, cucumber, broccoli)
- Tree nuts (hazelnuts, walnuts, almonds, cashews, almonds)
- Whole grain high-fibre foods (dried beans, peas, lentils, black beans)
- Dairy (cottage cheese, Greek yoghurt, cheese)
- Eggs
- Lean meat (chicken)
- Peanut butter
Monitor Your Blood Glucose Regularly
Monitoring your blood sugar with a home blood glucose monitor is a good way to keep your condition in check.
It helps you to assess how your food, stress levels, medication, exercise, and insulin injections are affecting your condition.
Diabetes Medication
There are a few types of common diabetes medications available for Type 2 diabetes.
These medications mostly work by lowering glucose production in your liver and boosting your body’s sensitivity to insulin. This way, your body can use insulin more effectively.
Other medications may help in the production of more insulin, reducing blood sugar levels, slowing down digestion, and more.
Visit the Diabetics and Metabolism Centre (DMC) in Singapore
The Diabetics and Metabolism Centre is a multi-disciplinary centre under the Singapore General Hospital where diabetic patients can visit for a comprehensive service.
Here, you can get clinical consultation, diabetes nurse education, dietetics counselling, and drug management services. It combines clinical care in different services that are specially curated to meet the needs of patients.
What Increases Your Risk of Developing Diabetes?
There are certain factors that can influence your risk of developing diabetes, like smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages frequently.

The risk of developing diabetes may differ for each group of people. We take a look at the 4 common groups of people at risk of diabetes:
| Type of Diabetes | What It Is | Risk Factors |
| Prediabetes | Blood glucose levels that are higher than the normal range but insufficient to be diagnosed as diabetes | – A sedentary and inactive lifestyle – Poor lifestyle choices like smoking and drinking alcohol – A family history of diabetes – High blood pressure – At least 40 years of age – History of gestational diabetes – High BMI of 23kg/m2 or more – Irregular blood cholesterol or lipid levels – Damaged glucose tolerance or fasting glucose |
| Type 1 Diabetes | A chronic condition where your pancreas cannot create insulin normally | – Family history of diabetes – Has pancreatic diseases – Genetics – Age (appears in 2 obvious peaks, between 4 and 7 years old, and the second between 10 and 14 years old) |
| Type 2 Diabetes | The most prevalent type of diabetes where your cannot cannot use insulin properly | – Same risk factors as prediabetes |
| Gestational Diabetes | Happens during pregnancy when pregnant women without diabetes have high blood glucose levels because of hormonal changes | – Family history of diabetes – Previously gave birth to a baby weighing 4kg or more upon delivery – Previously had gestational diabetes during a previous pregnancy |
What Do Low Levels of Blood Glucose Levels (Hypoglycemia) Mean?
Now, let’s go back to the topic of blood glucose, and take a look at the other end of the spectrum, hypoglycemia.
Hyperglycemia vs hypoglycemia – what’s the difference?
The opposite of high blood glucose levels is hypoglycemia, and this is also a condition that can lead to complications that affect your kidneys.
Low glucose levels are common in those with diabetes, both Type 1 and Type 2 (who consume insulin or other medications for diabetes). If you have diabetes, hypoglycemia is defined as having a reading of 70mg/dL or less.
What Are the Symptoms of Hypoglycemia?
Symptoms of low blood glucose can happen quickly and may differ from person to person.
Here are some common symptoms, classed into mild and serious categories:
| Mild | Serious |
| – Jittery – Fatigue – Hunger – Dizziness or lightheadedness – Irritable – Confusion – Rapid heartbeat – Unstable heartbeat – Headache – Unable to see or talk clearly | – Loss of consciousness – Seizure |
What Is the Best Diet for Hypoglycemia?
If you have hypoglycemia, how should you modify your diet to improve your condition?

Here are some recommended foods to eat:
- Whole grains and high-fibre food
- Protein (fish, eggs, low-fat cheese)
- Whole fruits (apples, bananas, oranges)
- Plant Fats (seeds, nuts, avocadoes, olive oil)
Please check with your doctor as everyone may have different health conditions.
Diet Tips for Hypoglycemia
There are a few dietary tips that you should take note of:
- Eat from a variety of food groups instead of just 1 type, like eating tofu with rice and vegetables
- Stagger your carbohydrate consumption throughout the day
- Have small meals or snacks spread throughout the day e.g. every 3 to 4 hours
- Limit your caffeine intake because it can imitate hypoglycemia symptoms
- Limit or steer away from alcohol completely because it can lead to hypoglycemia. If you drink alcohol, make sure you also eat at the same time
- Eat fats in small amounts






